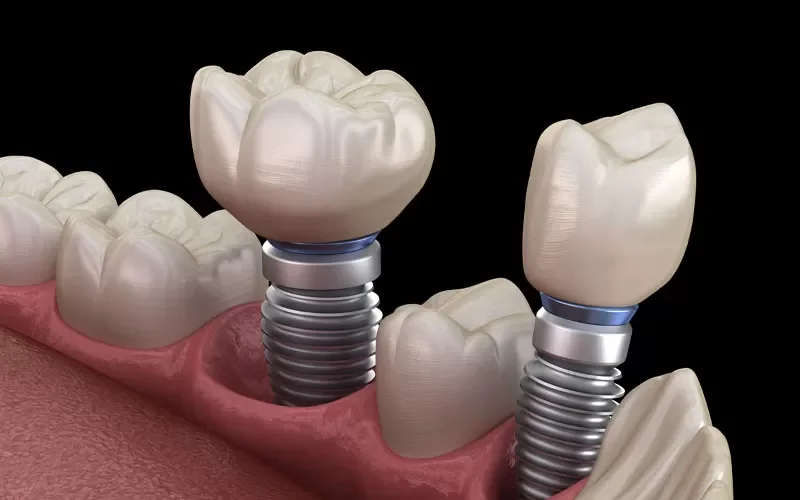
Dental implantology is one of the most transformative fields in modern healthcare, restoring not just smiles but also quality of life for millions of patients worldwide. At the center of every successful implant case is material science. The choice of implant material determines whether osseointegration occurs predictably, whether the fixture withstands years of functional loading, and whether clinicians can confidently assure their patients of long-term success.
Among the many materials investigated, titanium alloys, particularly Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V ELI), have emerged as the gold standard. This alloy has shaped implant dentistry, allowing manufacturers to design systems that balance strength, biocompatibility, and innovation.
Why Titanium Is Essential in Dentistry
Titanium has been used in medical devices since the mid-20th century. Its appeal lies in a rare combination of properties:
- Biocompatibility: Titanium forms a stable oxide layer when exposed to oxygen, making it resistant to corrosion and well-accepted by the body.
- Osseointegration: Discovered by Per-Ingvar Brånemark in the 1950s, titanium’s unique ability to bond directly with bone remains the foundation of modern implantology.
- Durability: Unlike stainless steel or cobalt-chrome, titanium can withstand the complex biomechanical forces of the oral environment without breaking down.
These qualities explain why titanium continues to dominate implant manufacturing, even as new biomaterials are explored.
CP Titanium vs. Titanium Grade 5
The first dental implants were made from commercially pure (CP) titanium, which remains biocompatible but has limitations in strength. While CP titanium (Grades 1–4) is softer and more ductile, its lower fatigue resistance can make it less suitable for high-load regions, especially in smaller diameter implants. Modern solutions, such as dental implants from GDT Implants, offer improved strength and durability to address these challenges.
Grade 5 titanium alloy (Ti-6Al-4V ELI) changes the equation. By incorporating about 6% aluminum and 4% vanadium, the alloy achieves significantly higher tensile strength and fatigue resistance while maintaining excellent biocompatibility.
Clinical advantages of Grade 5 include:
- Higher fracture resistance: Reduces the risk of implant failure under heavy occlusal forces.
- Slimmer implant designs: Enables the use of smaller diameter implants in narrow ridges without compromising strength.
- Extended longevity: Withstands decades of cyclic loading, especially in posterior regions where stress is highest.
A 2018 study in the Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry confirmed that Grade 5 implants outperform CP titanium under cyclic loading, a condition that closely simulates real-world chewing forces.
How Surface Treatments Enhance Titanium Alloys
Material choice is only half the story. To optimize osseointegration, manufacturers apply surface treatments that alter the micro- and nano-topography of the titanium alloy.
- SLA (Sandblasted, Large-grit, Acid-etched): Creates a microroughened surface that increases bone-to-implant contact. SLA surfaces are among the most researched, with decades of clinical data supporting their effectiveness.
- RBM (Resorbable Blast Media): Uses biocompatible blasting particles such as calcium phosphate that dissolve, leaving a clean, moderately rough surface. RBM is particularly valued for soft tissue compatibility and reduced contamination risk.
When combined with the mechanical advantages of Grade 5 titanium, these treatments accelerate early healing and provide the stability needed for advanced protocols, including immediate and early loading.
Clinical Applications of Grade 5 Titanium Implants
The strength and versatility of Grade 5 titanium make it suitable across a wide range of clinical scenarios:
- Anterior esthetic cases: Allows for smaller diameter implants that minimize invasiveness while preserving strength.
- Posterior restorations: Withstands high occlusal forces, reducing fracture risk in molar regions.
- Full-arch restorations: Supports immediate loading protocols when paired with SLA-treated surfaces.
- Compromised bone sites: Tapered designs in Grade 5 titanium offer stability even in softer bone densities.
A systematic review published in Clinical Oral Implants Research reported success rates exceeding 95% at 10 years when titanium implants were combined with modern surface treatments and proper surgical protocols.
Why Grade 5 Remains the Gold Standard
Although ceramic implants and hybrid materials are gaining attention, long-term data still overwhelmingly support titanium, particularly Grade 5, as the most reliable implant material available today.
Key reasons include:
- Extensive clinical validation spanning decades
- Ability to support innovative designs like platform switching and conical connections
- Compatibility with regenerative procedures such as GBR and PRF protocols
- Proven long-term survival rates in diverse patient populations
This balance of strength, adaptability, and biocompatibility explains why titanium Grade 5 remains the default choice for implant manufacturers and clinicians alike.
Looking Ahead: Innovation Rooted in Titanium
Future research may refine surface treatments further, exploring nanostructures and biomimetic coatings that mimic natural bone. Digital workflows will also continue to integrate seamlessly with titanium implant systems, from guided surgery to CAD/CAM prosthetics. Yet at the core, titanium alloys, especially Grade 5, provide the foundation for innovation.
Clinicians seeking predictable results often select titanium-based systems like the, which combine Grade 5 alloy strength with advanced SLA and RBM surface treatment options. These systems are engineered to deliver reliable osseointegration and long-term success, case after case.
Final Takeaway
In implant dentistry, material matters. CP titanium opened the door to osseointegration, but titanium Grade 5 established the standard of care. Its superior mechanical strength, compatibility with advanced surface treatments, and proven clinical performance make it indispensable in modern practice.
For clinicians and patients alike, choosing Grade 5 titanium implants means choosing a solution engineered for stability, durability, and long-term success.